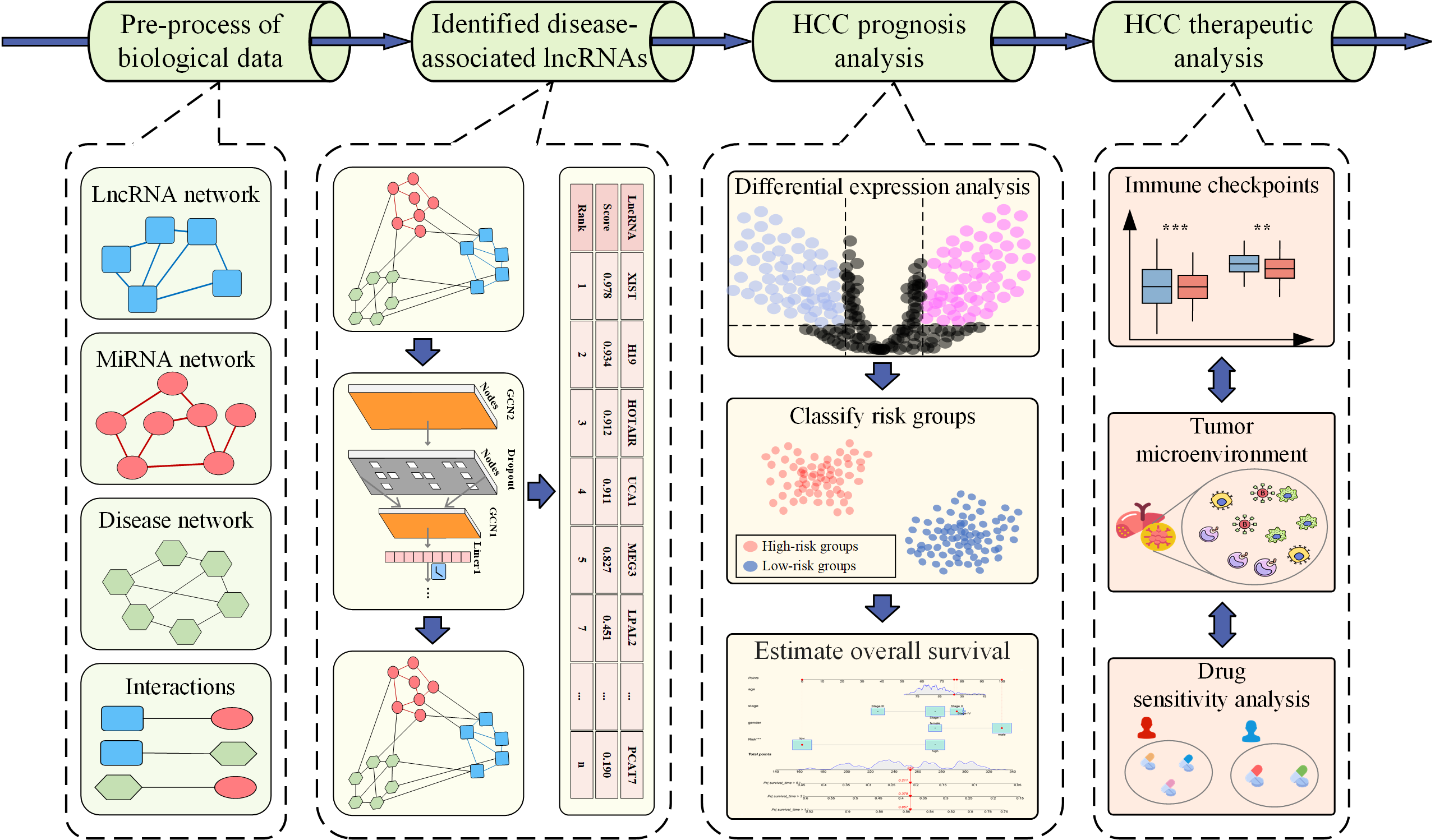
Introduction
Exploring disease mechanism at the molecular level provides valuable guidance for disease prognosis and therapy, and most researches mainly focused on the genetic or protein levels. However, the emergence and progression of complex diseases are intricately linked to lncRNAs, and comprehensive analysis of complex diseases from the lncRNA perspective has been rarely explored. In this end, A systemic pipeline is proposed, which aims to identify disease-associated lncRNAs to prognosis and treatment of HCC. More specifically, due to the importance of identifying disease-associated lncRNA and the weak interpretability of existing computational identification methods, we propose a novel approach named iLncDA-PT to identify disease-associated lncRNAs considering the interactions between various bio-entities, and then we conduct a systematically molecular pathogenesis analysis on prognosis and therapy for specific disease, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as an example. Finally, we reveal a significant association between immune checkpoint expression, tumor microenvironment, and drug treatment.